The Importance of Measuring Data Center Performance and How to Get Started
The answer depends on whom you ask. To upper management, the answer is likely all of the above. In this article, I’d like to discuss the importance of measuring data center performance and how operators can begin to tackle “all of the above” by using a quantifiable, science-backed methodology.
Competing Demands Exacerbate Data Center Performance Issues
Data center operators are regularly tasked with delivering more processing throughput in less space in a sustainable fashion. This is easier said than done when considering the conflicting demands facing operators.
The proliferation of high-performance applications and high-density IT equipment increases pressure on the data center system. Mixed-density IT equipment can create demands for power and cooling resources that facilities—especially legacy facilities—are unable to accommodate. Adding to this challenge is the fact that current data center management tools and techniques lack the ability to predict the impact of operational changes, such as deploying high-density IT hardware, on the data center’s ability to power and cool the IT configuration. This can leave operators with no choice but to overcompensate on resource provisions to counteract this risk.
In turn, overcompensating on these resources can negatively impact carbon emissions and energy costs. Sustainability regulations, such as the Energy Efficiency Directive, are on the horizon. These regulations will place additional pressure on operators to track, report, and inevitably reduce power and cooling provisions without increasing the risk of power- or cooling-related failures. Given these competing demands, how should operators approach the delicate balancing act that is data center performance?
Some teams will suggest focusing on space usage improvements, while others will be more concerned about the longevity of IT equipment, the carbon footprint, the OpEx, and the list goes on. The best way to understand which of these competing demands to tackle first is to measure the data center’s performance. Doing so illuminates which concerns are having the greatest impact, as well as the interconnected relationship between each demand.
We’ve found great success using The Green Grid’s Performance Indicator (PI) plus computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation to measure and improve data center performance.
How to Measure Data Center Performance
The Green Grid’s PI quantifies data center efficiency and the ability to meet IT cooling requirements. This provides a balanced understanding of data center performance and addresses how conflicting data center performance metrics impact one another. CFD simulation models complex thermals and cooling, which operators can use to validate operational decisions virtually before physical implementation.
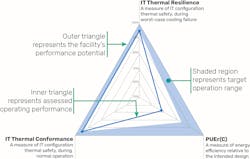
The Green Grid’s PI helps visualize the balance between achieving effective cooling during normal operation (IT Thermal Conformance) and adequate cooling during failure or maintenance within design parameters (IT Thermal Resilience), without compromising efficiency (PUE ratio), illustrated in the figure below.
The Green Grid’s PI considers the future effect of proposed changes before implementation of IT deployments. This methodology, plus CFD simulation, can provide a more complete understanding of the impact layout changes will have on operations.
With each new deployment, a data center’s layout changes from the original design. Even with the same total cooling, two different layouts can produce drastically different performance results. Using The Green Grid’s PI and a CFD-powered data center digital twin, operators can plan, test, and validate operational changes before physical implementation, while also considering sustainability metrics.
Measure, Test, and Improve Data Center Performance
Small, targeted adjustments to data center operations can have a significant impact on utilizing data center space effectively while working towards greater energy efficiency. Discovering these adjustments starts with measuring data center performance.
Measuring data center performance is easier and more effective when using a quantifiable methodology, such as The Green Grid’s PI, and science-backed data, like CFD simulation. When done correctly, a performance assessment is the first step toward understanding how to balance the conflicting parameters of data center performance.
Sherman Ikemoto is System Sales Group Director at Cadence Design Systems. Contact Cadence to learn more.