How Immersion Cooling is Changing Data Center Density and Design
This launches our article series on the fundamental shift that's taking place in the way the data center industry approaches cooling.
You won’t need to look too far back to realize just how key critical infrastructure is to our everyday lives. Data center ecosystems work hard to keep everyone connected, operational, and productive. Over the past few years, we’ve seen density levels rise as organizations are tasked to deliver more capacity with limited space.
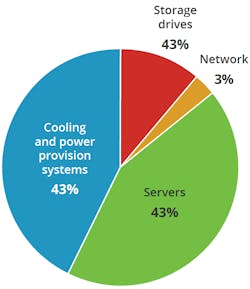
Considering this, the evolution of efficiency, density, and functional design must change. Leaders in the data center and colocation space have turned their attention to immersion cooling technologies that have proven highly effective and efficient and deliver new capabilities for critical infrastructure. Looking at costs specifically, data center leaders must zero in on cost efficiency and workload density. It’s a big reason many leverage immersion cooling to reduce data center OPEX by over 90% and reduce CAPEX costs by more than 50%.
This article series will explore the fundamental shift happening in our data center industry. Specifically, we’ll explore the evolution of immersion cooling and how data center leaders use this technology to achieve new efficiency imperatives.
Introduction
How we design and build critical infrastructure has changed so much over the past few years. One thing is for sure: Data centers aren’t going anywhere, and demand is increasing sharply due to various new use cases.
We see continual changes in reach density, in both heat and power, to keep up with high-performance computing (HPC) trends, which include Artificial Intelligence, Automation, and Machine Learning.
Here’s the other key challenge: Many current solutions can only sustain power requirements, heating production increases, and future flexibility for so long. There are new demands around cloud computing, big data, and infrastructure power/cooling efficiency. With advancements in new use cases and demand and the rapid growth in data leading the way within many technological categories – working with the right data center technologies has become more critical than ever.
This means new imperatives exist in how we cool, maintain, and optimize our data center facilities.
A COOLER WAY TO USE IMMERSION COOLING IN THE DATA CENTER
Immersion Cooling isn’t anything new; however, recent technological advancements have allowed more data centers to adopt the technology.
Why is this happening? Rising investments in high- density technology, high-performance computing, and data-driven workloads have pushed data center leaders to design the most reliable and efficient methods to cool their data centers. Today, data centers consume about 2-3 percent of global energy. However, according to the latest findings from the IEA, data centers and data transmission networks are responsible for nearly 1% of energy-related GHG emissions. Since 2010, emissions have grown modestly despite rapidly growing demand for digital services, thanks to energy efficiency improvements, renewable energy purchases by information and communications technology (ICT) companies, and broader decarbonization of electricity grids in many regions. Solutions like immersion cooling help reduce carbon footprint by removing water waste and revolutionizing heat dissipation.
It’s critical to note that business and data center developments have pushed immersion cooling into the forefront of infrastructure design. Let’s explore a few of these new developments:
- Data centers are using more power. According to a recent post from the IEA, digital technologies have direct and indirect effects on energy use and emissions and hold enormous potential to help (or hinder) global clean energy transitions, including through the digitalization of the energy Today, data centers and data transmission networks are responsible for nearly 1% of energy- related GHG emissions. Furthermore, a recent US Department of Energy report indicates that US data centers are projected to increase the amount of energy they consume based on current trend estimates. A trend that’s been steadily rising since 2000.
- HPC, AI, and data-driven solutions require a new approach. Here’s a specific example. High- performance computing (HPC) is being leveraged for research and data analysis, and these systems are being deployed within traditional data center However, cooling for HPC systems requires a different kind of approach. Immersion cooling helps dissipate heat from heavily used HPC systems and supports more significant density levels. The growth in data-driven solutions has directly impacted how data center leaders view cooling critical systems. It’s a big reason immersion cooling and immersion-ready technologies have supported emerging use cases.
Innovation around immersion-cooled data centers and specific use cases doesn’t stop at HPC. Emerging requirements around machine learning, financial services, healthcare, CAD modeling, and rendering are exploring new immersion-cooled solutions to maintain sustainability, reliability, and the greatest density levels.
A recent report from Technavio indicates that the adoption of immersion cooling is growing as it is considered more efficient than air-based cooling. Liquid-based cooling, a sub-segment of immersion liquid-based cooling, is the most widely accepted cooling system. Finally, Dell EMC’s study on the efficiency and liquid cooling dove into the cost of cooling data centers and how it impacts operators’ overall operating expenses. 50% responded that it had a significant impact, and 78% responded that there was at least some impact on their costs.
The survey also showed us that 25% already use liquid cooling in production environments, and 32% use liquid cooling in some fashion within their data center.
As the survey points out, there are many great ways to use liquid cooling within the data center.
- 39% have liquid cooling technologies within high- density cabinets or racks
- 20% deploy liquid cooling for high-performance computing (HPC) use cases
- 17% use it for big data processing
- 15% already have full-package systems where the majority of the heat is removed through liquid
More of your customers will be asking for highly dense, compute-intensive solutions. Can today’s air-cooled ecosystems keep up? Immersion cooling has pushed boundaries on efficiency and density. Today, these solutions are a bridge to delivering the most advanced workloads to your customers.
Download the full report, New Data Center Efficiency Imperatives: How Immersion Cooling is Evolving Density and Design, featuring Hypertech, to learn more. In our next article, we'll dive into how immersion cooling changes data center design and how immersion cooling solutions today are much different than ever before, making adoption far more feasible.
About the Author